In today’s digital era, navigation seems effortlessopen a map app, check your location, and move confidently from one point to another. But behind this everyday convenience lies one of the most impactful technological innovations of the modern world: GPS. And one of the questions often asked by students, researchers, and technology enthusiasts is: who invented the GPS technology?
To answer this clearly, we must explore the science, the minds behind it, and the historical events that shaped the Global Positioning System into what it is today.
Table of Contents
Introduction: Why GPS Matters Today
GPS (Global Positioning System) is a satellite-based navigation system that helps determine a person’s exact location anywhere on Earth. It is used in:
- Smartphones
- Cars and transportation systems
- Military operations
- Aviation and marine navigation
- Agriculture
- Emergency response
- Logistics and delivery services
- Weather monitoring
- Scientific research
This technology has transformed billions of lives. But to truly understand who invented the GPS technology, we need to rewind the clock to mid-20th-century scientific breakthroughs, international conflicts, and the vision of engineers who believed that precise location tracking would one day serve all humanity.
Who Invented the GPS Technology? The Short Answer
Although many minds contributed to its development, three key scientists are officially recognized as the principal inventors of GPS:
1. Dr. Ivan A. Getting – The Visionary Behind GPS
- An American physicist and engineer
- Introduced the original concept of a satellite-based navigation system
- Played a crucial role in guiding the U.S. Air Force to adopt GPS
2. Dr. Bradford Parkinson – “The Father of GPS”
- Led the engineering team that designed and tested the first GPS satellites
- Oversaw the creation of the first working GPS prototype
- His leadership transformed an idea into a global navigation reality
3. Roger L. Easton – The Scientific Mind Behind Satellite Tracking
- Inventor of advanced satellite timing and navigation systems
- Created the technology used for tracking objects in space
- His work on time synchronization is a fundamental GPS building block
So, who invented the GPS technology?
➡️ It was the combined work of Dr. Ivan Getting, Dr. Bradford Parkinson, and Roger Easton, with large-scale support from the U.S. Department of Defense.
The Origin Story: How the Idea of GPS Was Born
To fully understand the invention, we must look at the world events and scientific achievements that inspired the invention of GPS.

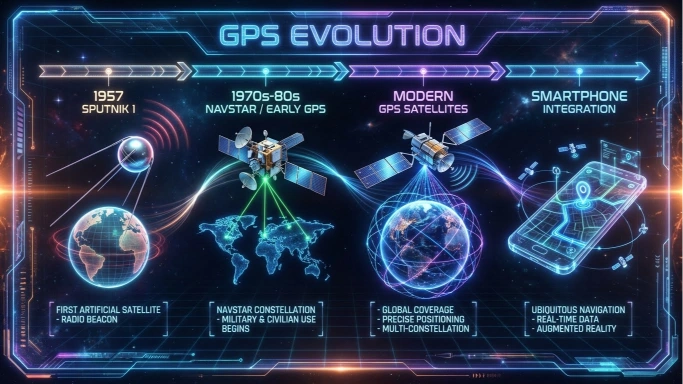
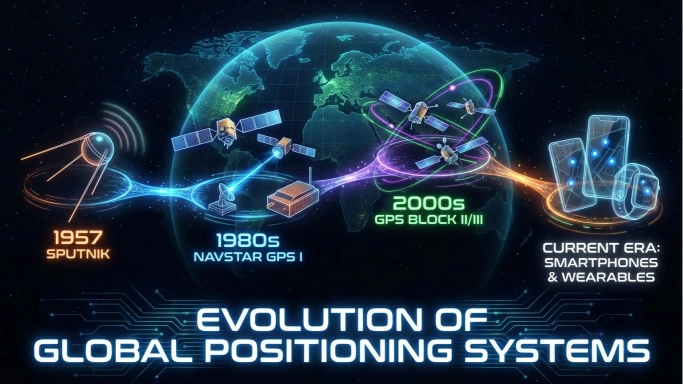
1. The Launch of Sputnik (1957)
When the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the world’s first satellite, American scientists were surprised by the signal it kept sending from space. Two physicists at MIT, William Guier and George Weiffenbach, discovered that they could track the satellite’s position based on shifts in radio frequency (the Doppler effect).
This became the first time scientists realized:
“If you know the position of a satellite, you can find your own location on Earth.”
This discovery laid the foundation of satellite navigation.
2. Early Navigation Systems Before GPS
Before GPS, there were several military navigation systems such as:
- TRANSIT (U.S. Navy)
- LORAN (Long Range Navigation)
- Timation satellites (experimental tracking by Roger Easton)
These systems lacked accuracy, speed, and global coverage. The military needed something faster, more reliable, and worldwide.
That became the birth of the modern GPS concept.
Dr. Ivan Getting: The Original Brain Behind GPS
Dr. Ivan Getting was a prominent engineer who strongly advocated for a unified satellite navigation system. As the president of The Aerospace Corporation, he insisted that America needed:
- A highly accurate
- Fully global
- All-weather
- Real-time navigation solution
His ideas convinced the Department of Defense to fund what would become the NAVSTAR GPS program in the 1970s.
Even though he was not the sole creator, he was the conceptual father of GPS.
Roger L. Easton: The Master of Satellite Tracking & Timing
Easton’s contributions were extremely important because GPS depends on highly precise time measurements.
His inventions included:
- The Timation satellite program
- Atomic clock synchronization in space
- Numerical tracking techniques for satellites
GPS accuracy (within meters or centimeters) is possible only because Easton solved the problem of satellite time coordination. Without him, GPS could never have existed.
Dr. Bradford Parkinson: The Father of GPS
If Easton and Getting were the scientific foundations, then Parkinson was the architect who turned the idea into a working technology.
As the program director for NAVSTAR GPS, Parkinson:
- Built the first working GPS satellite
- Developed the first GPS receivers
- Led the team that demonstrated GPS in real-world tests
- Fought for funding, testing, and government approval
He is widely known as “The Father of GPS” because he transformed theory into practice.
Why Was GPS Invented? The Real Reason Behind It
Although today GPS helps us find a restaurant or track a parcel, the original purpose was military.
The U.S. military needed:
- Better navigation for aircraft
- Missile guidance
- Improved troop coordination
- Real-time positioning during war
During the Cold War, accurate navigation became a matter of national security. GPS was developed to give the U.S. military a strategic advantage.
When Was GPS Invented? A Timeline
Let’s look at the development timeline:
1957
Sputnik launches → First satellite tracking experiment.
1960–1970
TRANSIT and Timation systems built.
1973
NAVSTAR GPS project officially approved.
1978
First experimental GPS satellite launched.
1983
Korean Air Lines Flight 007 accidentally entered Soviet airspace and was shot down.
➡️ After this tragedy, the U.S. government opened GPS for civilian use.
1995
GPS declared fully operational with 24 satellites.
2000
Selective Availability (artificial GPS error for civilians) turned off.
➡️ Civilian GPS accuracy improved dramatically.
Today
GPS is used in smartphones, cars, aviation, shipping, agriculture, and more.
How GPS Technology Works: A Simple Explanation
GPS works using a network of 24–32 satellites orbiting Earth. Each satellite contains:
- A high-precision atomic clock
- A transmitter that sends constant signals
Here’s how your phone determines your location:
Step 1: Satellites send time-stamped signals
Each satellite broadcasts the exact time and its position.
Step 2: Your device receives the signals
Your smartphone listens to signals from multiple satellites.
Step 3: Device calculates distance
By measuring how long signals took to reach you, it calculates how far you are from each satellite.
Step 4: Triangulation
With data from at least four satellites, your phone can determine:
- Your latitude
- Your longitude
- Your altitude
- Your movement speed
- Your direction
This process happens in milliseconds.
Civilian vs Military GPS: Are They the Same?
Originally, GPS was only for military use. Civilians got access after 1983, but with lower accuracy. After 2000, the U.S. government removed limitations, making GPS highly accurate for everyone.
The military still uses an encrypted, more precise GPS network.

Impact of GPS on Everyday Life
Today, GPS is everywhere. Here are the industries it transformed:
1. Transportation & Navigation
GPS powers:
- Google Maps
- Uber and Careem
- Food delivery apps
- Fleet tracking
Millions of people rely on GPS to travel safely.
2. Agriculture
Farmers use GPS for:
- Crop planning
- Soil mapping
- Tractor automation
- Water management
This is called Precision Agriculture.
3. Aviation & Marine
Airplanes and ships depend entirely on GPS for:
- Safe navigation
- Weather tracking
- Landing assistance
- Collision avoidance
4. Emergency Services
911 and rescue teams use GPS to locate:
- Accident victims
- Lost hikers
- Hazard zones
Time saved = lives saved.
5. Science & Space Exploration
GPS is used in:
- Earthquake prediction
- Climate research
- Spacecraft tracking
It is a fundamental scientific tool.
The Future of GPS Technology
GPS continues to evolve. Future improvements include:
- Even more accurate positioning (centimeter-level)
- Integration with AI and autonomous vehicles
- Better indoor navigation
- Cross-compatibility with other systems (GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo)
- Quantum-based timing systems
Soon, self-driving cars and delivery drones will depend heavily on hyper-accurate GPS.
Conclusion: Who Invented the GPS Technology?
So, who invented the GPS technology?
GPS was not created by one personit was the combined achievement of:
- Dr. Ivan Getting – Visionary founder
- Roger L. Easton – Satellite tracking & timing pioneer
- Dr. Bradford Parkinson – Leader and “Father of GPS”
Supported by decades of scientific research and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, GPS evolved from a military tool into an essential part of modern life.
Today, billions of people depend on GPS without even realizing the brilliance and history behind it.